Guard Against Phishing Scams
When using crypto products such as wallets and exchanges, protecting the security of your assets is the No.1 priority. In “CoinEx Wallet Security Tips”, we will share some basic crypto know-how such as common scams, how to use crypto products safely, and blockchain security mechanisms from multiple perspectives to help you fully understand asset security and adopt enhanced protection measures.
In recent years, phishing has become an increasingly prevalent crypto scam. Other than emails, scammers have also started to use media and instant messaging software to run their tricks. As crypto users, we should learn how to identify phishing scams and stay on alert.
1. What is aphishing scam
Phishing (homonymous with fishing) is a type of fraud where scammers attempt to acquire sensitive information such as user names and passwords via electronic communications by disguising themselves as a reputable institution.
When communicating with victims, scammers often claim to be the employees of popular social networking sites and banks or network administrators to gain users’ trust. Phishing is usually conducted through emails or instant messaging services. Such scams often direct users to submit personal information on a fake website that’s almost identical to the real one.
As cryptocurrencies keep growing, the crypto space has also become the target of phishing scammers. For example, they would pretend to be employees of CoinEx Exchange or CoinEx Wallet and trick users into submitting their personal information on a fake website they provide (one that looks almost exactly the same as the real one) via emails, social networking sites, or instant messaging software to acquire sensitive information such as the account number and the private key.
Plenty of phishing websites have popped up in the NFT market, which has boomed over recent years. Such websites are made at cheap costs, and scammers have built a standardized and professional industry chain. Such scammers often use certain tools to copy the website of well-known NFT projects to trick users into submitting their mnemonic phrases or offering authorization.
2. Common types of phishing scams and cases
2.1 Email phishing scams
Our personal information, including email addresses and phone numbers, is frequently leaked. Scammers would first obtain a victim’s email address through certain channels and then pretend to be the employees of some crypto exchange. Next, they would send a fake link disguised as an exchange website to users and trick the victims into opening the link and filling in their personal information.
Scammers often claim that they are employees of a crypto exchange in emails. They’d say that the exchange is now offering airdrop rewards, but they’ll need to verify the victim’s asset status before distributing the tokens. The victim would be asked to offer his account name and private key for verification. In fact, the link provided in such emails are fake websites built by the scammers, and once he enters his personal information such as the password and the private key, the scammers would empty his wallet.
2.2 SNS phishing scams
As crypto categories like DeFi and NFT expand, a growing number of users are flocking to the crypto sector. Meanwhile, the information of many NFT airdrops is available on mainstream SNS sites like Twitter. As such, some scammers would release fake news on Twitter and run their scams by asking users to provide personal information such as their private keys.
For example, scammers could register an account that looks similar to the official Twitter account of a crypto exchange or NFT marketplace. In some cases, the fake name might be exactly the same as the real one except for only one letter. They would then start posting scam messages to lure users into providing their personal information.
Scammers might also hack the Twitter account of a crypto big shot and post scam messages that seem normal to run their scams. For instance, the Twitter account of Beeple, a crypto artist with over 670,000 followers, was once hacked, and the scammers got $440,000 worth of ETH from the hack.
Moreover, the Twitter account of many US politicians and business leaders had all been hacked for posting phishing messages.
2.3 Phishing scams via instant messaging software
Many crypto platforms and projects have created groups on Telegram and Discord for communication and events. A large number of crypto users, including scammers, are active in such groups.
Scammers would pretend to be employees of a project and then send phishing messages to users through direct messages, tricking them into providing their personal information at a fake website.
3. How to identify and guard against phishing scams
3.1 All operations must be carried out on the official website or APP
Users should keep their accounts safe and secure at all times. To that end, they should avoid scanning QR codes that are not from the official channel. Users should refrain from clicking on unknown links or logging in to unsafe websites to prevent the disclosure of personal information like account numbers and passwords, which might result in unnecessary losses.
For example, when using CoinEx Wallet, users should conduct all operations on the official CoinEx Wallet website or APP. Be sure to check the URL(https://wallet.coinex.com/) and download the APP on the official website.
3.2 Set up the anti-phishing code
The anti-phishing code is a security feature that allows users to enhance account security, thereby better protecting their assets. The function is available on many crypto exchanges, say, CoinEx.
Once you create the anti-phishing code, all the official emails will contain the anti-phishing code you set, so that you can tell whether it’s an official email or not and thus avoid phishing scams.
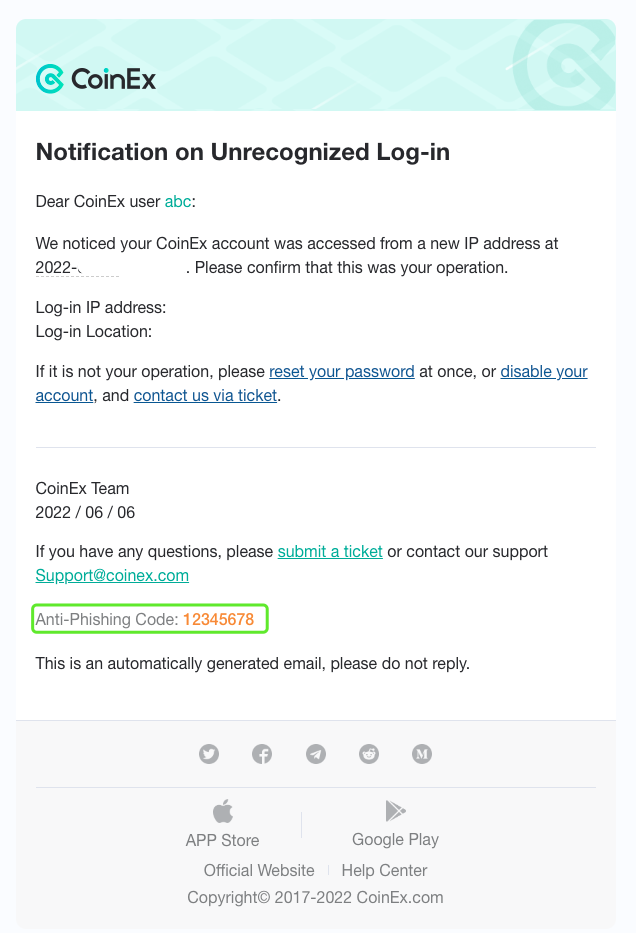
Note: Do not disclose your anti-phishing code to anyone, including the official customer service employees.
3.3 Remember the official SNS account
To expand their influence, project teams often create SNS accounts on platforms like Twitter, Telegram, and Discord. Users need to remember the official account and social media groups, which are often available on the official website of the project.
In a nutshell, whether you plan to trade on an exchange or make a transfer in a wallet, be sure to go to the official website or APP. In addition, do not scan any non-official QR codes, and stay away from links from unknown sources and unsafe websites. Also, do remember the official SNS accounts, including Twitter, Discord, and Telegram, of a project. Lastly, please keep your account information safe, and do not disclose it to anyone else.








